Stroke outcome#
The stroke outcome model is used in lots of our projects relating to stroke. To make it easier to share the model across so many places, the python code has been placed in a code package.
These chapters provide some basic working examples for the stroke-outcome package.
Source code: stroke-modelling/stroke-outcome
PyPI package: https://pypi.org/project/stroke-outcome/
📦 Package details:#
The package includes the following data:
mRS cumulative probability distributions as derived in [the online book][jupyterbooks-link].
A selection of utility scores for each mRS level.
Optionally, other data can be used instead of these provided files. The required formats are described in the continuous outcome demo.
The package includes the following processes:
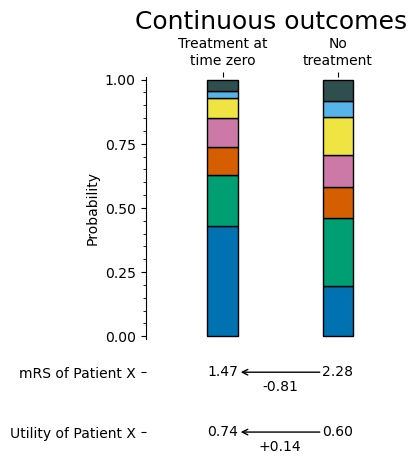
Continuous outcomes: Each “patient” uses the average mRS across a population mRS probability distribution. The average mRS score may be any number between 0 and 6, for example 1.2.
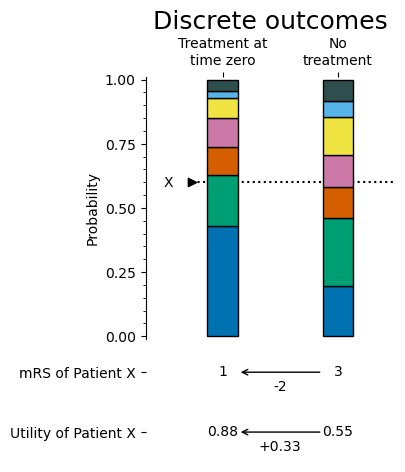
Discrete outcomes: Each patient is given a single mRS score out of the population mRS probability distribution. The score must be a whole number from 0 to 6.
The following images summarise the differences between the methods: