Logistic Regression Classifier - Fitting to all stroke teams together
Contents
Logistic Regression Classifier - Fitting to all stroke teams together#
Aims#
Assess accuracy of a logistic regression classifier, using k-fold (5-fold) training/test data splits (each data point is present in one and only one of the five test sets). This notebook fits all data in a single model, with hospital ID being a one-hot encoded feature.
The notebook includes:
A range of accuracy scores
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and Sensitivity-Specificity Curves
Identify feature weights (model coefficients)
Performing a learning rate test (relationship between training set size and accuracy)
Import libraries#
# Turn warnings off to keep notebook tidy
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import auc
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
Import data#
Data has previously been split into 5 training/test splits.
data_loc = '../data/kfold_5fold/'
train_data, test_data = [], []
for i in range(5):
train_data.append(pd.read_csv(data_loc + 'train_{0}.csv'.format(i)))
test_data.append(pd.read_csv(data_loc + 'test_{0}.csv'.format(i)))
Functions#
Standardise data#
Standardisation subtracts the mean and divides by the standard deviation, for each feature. Here we use the sklearn built-in method for standardisation.
def standardise_data(X_train, X_test):
"""
Converts all data to a similar scale.
Standardisation subtracts mean and divides by standard deviation
for each feature.
Standardised data will have a mena of 0 and standard deviation of 1.
The training data mean and standard deviation is used to standardise both
training and test set data.
"""
# Initialise a new scaling object for normalising input data
sc = StandardScaler()
# Set up the scaler just on the training set
sc.fit(X_train)
# Apply the scaler to the training and test sets
train_std=sc.transform(X_train)
test_std=sc.transform(X_test)
return train_std, test_std
Calculate accuracy measures#
def calculate_accuracy(observed, predicted):
"""
Calculates a range of accuracy scores from observed and predicted classes.
Takes two list or NumPy arrays (observed class values, and predicted class
values), and returns a dictionary of results.
1) observed positive rate: proportion of observed cases that are +ve
2) Predicted positive rate: proportion of predicted cases that are +ve
3) observed negative rate: proportion of observed cases that are -ve
4) Predicted negative rate: proportion of predicted cases that are -ve
5) accuracy: proportion of predicted results that are correct
6) precision: proportion of predicted +ve that are correct
7) recall: proportion of true +ve correctly identified
8) f1: harmonic mean of precision and recall
9) sensitivity: Same as recall
10) specificity: Proportion of true -ve identified:
11) positive likelihood: increased probability of true +ve if test +ve
12) negative likelihood: reduced probability of true +ve if test -ve
13) false positive rate: proportion of false +ves in true -ve patients
14) false negative rate: proportion of false -ves in true +ve patients
15) true positive rate: Same as recall
16) true negative rate: Same as specificity
17) positive predictive value: chance of true +ve if test +ve
18) negative predictive value: chance of true -ve if test -ve
"""
# Converts list to NumPy arrays
if type(observed) == list:
observed = np.array(observed)
if type(predicted) == list:
predicted = np.array(predicted)
# Calculate accuracy scores
observed_positives = observed == 1
observed_negatives = observed == 0
predicted_positives = predicted == 1
predicted_negatives = predicted == 0
true_positives = (predicted_positives == 1) & (observed_positives == 1)
false_positives = (predicted_positives == 1) & (observed_positives == 0)
true_negatives = (predicted_negatives == 1) & (observed_negatives == 1)
false_negatives = (predicted_negatives == 1) & (observed_negatives == 0)
accuracy = np.mean(predicted == observed)
precision = (np.sum(true_positives) /
(np.sum(true_positives) + np.sum(false_positives)))
recall = np.sum(true_positives) / np.sum(observed_positives)
sensitivity = recall
f1 = 2 * ((precision * recall) / (precision + recall))
specificity = np.sum(true_negatives) / np.sum(observed_negatives)
positive_likelihood = sensitivity / (1 - specificity)
negative_likelihood = (1 - sensitivity) / specificity
false_positive_rate = 1 - specificity
false_negative_rate = 1 - sensitivity
true_positive_rate = sensitivity
true_negative_rate = specificity
positive_predictive_value = (np.sum(true_positives) /
(np.sum(true_positives) + np.sum(false_positives)))
negative_predictive_value = (np.sum(true_negatives) /
(np.sum(true_negatives) + np.sum(false_negatives)))
# Create dictionary for results, and add results
results = dict()
results['observed_positive_rate'] = np.mean(observed_positives)
results['observed_negative_rate'] = np.mean(observed_negatives)
results['predicted_positive_rate'] = np.mean(predicted_positives)
results['predicted_negative_rate'] = np.mean(predicted_negatives)
results['accuracy'] = accuracy
results['precision'] = precision
results['recall'] = recall
results['f1'] = f1
results['sensitivity'] = sensitivity
results['specificity'] = specificity
results['positive_likelihood'] = positive_likelihood
results['negative_likelihood'] = negative_likelihood
results['false_positive_rate'] = false_positive_rate
results['false_negative_rate'] = false_negative_rate
results['true_positive_rate'] = true_positive_rate
results['true_negative_rate'] = true_negative_rate
results['positive_predictive_value'] = positive_predictive_value
results['negative_predictive_value'] = negative_predictive_value
return results
Find model probability threshold to match predicted and actual thrombolysis use#
def find_threshold(probabilities, true_rate):
"""
Find classification threshold to calibrate model
"""
index = (1-true_rate)*len(probabilities)
threshold = sorted(probabilities)[int(index)]
return threshold
Line intersect#
Used to find point of sensitivity-specificity curve where sensitivity = specificity.
def get_intersect(a1, a2, b1, b2):
"""
Returns the point of intersection of the lines passing through a2,a1 and b2,b1.
a1: [x, y] a point on the first line
a2: [x, y] another point on the first line
b1: [x, y] a point on the second line
b2: [x, y] another point on the second line
"""
s = np.vstack([a1,a2,b1,b2]) # s for stacked
h = np.hstack((s, np.ones((4, 1)))) # h for homogeneous
l1 = np.cross(h[0], h[1]) # get first line
l2 = np.cross(h[2], h[3]) # get second line
x, y, z = np.cross(l1, l2) # point of intersection
if z == 0: # lines are parallel
return (float('inf'), float('inf'))
return (x/z, y/z)
Fit model (k-fold)#
# Set up list to store models and calibarion threshold
single_models = []
thresholds = []
# Set up lists for observed and predicted
observed = []
predicted_proba = []
predicted = []
# Set up list for feature weightsd
feature_weights = []
# Loop through k folds
for k_fold in range(5):
# Get k fold split
train = train_data[k_fold]
test = test_data[k_fold]
# Get X and y
X_train = train.drop('S2Thrombolysis', axis=1)
X_test = test.drop('S2Thrombolysis', axis=1)
y_train = train['S2Thrombolysis']
y_test = test['S2Thrombolysis']
# One hot encode hospitals
X_train_hosp = pd.get_dummies(X_train['StrokeTeam'], prefix = 'team')
X_train = pd.concat([X_train, X_train_hosp], axis=1)
X_train.drop('StrokeTeam', axis=1, inplace=True)
X_test_hosp = pd.get_dummies(X_test['StrokeTeam'], prefix = 'team')
X_test = pd.concat([X_test, X_test_hosp], axis=1)
X_test.drop('StrokeTeam', axis=1, inplace=True)
# Standardise X data
X_train_std, X_test_std = standardise_data(X_train, X_test)
# Define and Fit model
model = LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs')
model.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
# Get feature weights
weights = model.coef_[0]
feature_weights.append(weights)
# Get predicted probabilities
y_probs = model.predict_proba(X_test_std)[:,1]
observed.append(y_test)
predicted_proba.append(y_probs)
# Calibrate model and get class
true_rate = np.mean(y_test)
threshold = find_threshold(y_probs, true_rate)
thresholds.append(threshold)
y_class = y_probs >= threshold
y_class = np.array(y_class) * 1.0
predicted.append(y_class)
# Print accuracy
accuracy = np.mean(y_class == y_test)
print (
f'Run {k_fold}, accuracy: {accuracy:0.3f}, threshold {threshold:0.3f}')
Run 0, accuracy: 0.833, threshold 0.474
Run 1, accuracy: 0.834, threshold 0.475
Run 2, accuracy: 0.830, threshold 0.469
Run 3, accuracy: 0.833, threshold 0.470
Run 4, accuracy: 0.833, threshold 0.470
Results#
Accuracy measures#
# Set up list for results
k_fold_results = []
# Loop through k fold predictions and get accuracy measures
for i in range(5):
results = calculate_accuracy(observed[i], predicted[i])
k_fold_results.append(results)
# Put results in DataFrame
single_fit_results = pd.DataFrame(k_fold_results).T
single_fit_results
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| observed_positive_rate | 0.295232 | 0.295401 | 0.295176 | 0.295080 | 0.295417 |
| observed_negative_rate | 0.704768 | 0.704599 | 0.704824 | 0.704920 | 0.704583 |
| predicted_positive_rate | 0.295232 | 0.295457 | 0.295176 | 0.295080 | 0.295417 |
| predicted_negative_rate | 0.704768 | 0.704543 | 0.704824 | 0.704920 | 0.704583 |
| accuracy | 0.832565 | 0.833858 | 0.830316 | 0.833343 | 0.833455 |
| precision | 0.716435 | 0.718744 | 0.712571 | 0.717607 | 0.718120 |
| recall | 0.716435 | 0.718881 | 0.712571 | 0.717607 | 0.718120 |
| f1 | 0.716435 | 0.718812 | 0.712571 | 0.717607 | 0.718120 |
| sensitivity | 0.716435 | 0.718881 | 0.712571 | 0.717607 | 0.718120 |
| specificity | 0.881213 | 0.882062 | 0.879627 | 0.881790 | 0.881813 |
| positive_likelihood | 6.031237 | 6.095409 | 5.919679 | 6.070604 | 6.076135 |
| negative_likelihood | 0.321790 | 0.318707 | 0.326762 | 0.320250 | 0.319660 |
| false_positive_rate | 0.118787 | 0.117938 | 0.120373 | 0.118210 | 0.118187 |
| false_negative_rate | 0.283565 | 0.281119 | 0.287429 | 0.282393 | 0.281880 |
| true_positive_rate | 0.716435 | 0.718881 | 0.712571 | 0.717607 | 0.718120 |
| true_negative_rate | 0.881213 | 0.882062 | 0.879627 | 0.881790 | 0.881813 |
| positive_predictive_value | 0.716435 | 0.718744 | 0.712571 | 0.717607 | 0.718120 |
| negative_predictive_value | 0.881213 | 0.882132 | 0.879627 | 0.881790 | 0.881813 |
single_fit_results.T.describe()
| observed_positive_rate | observed_negative_rate | predicted_positive_rate | predicted_negative_rate | accuracy | precision | recall | f1 | sensitivity | specificity | positive_likelihood | negative_likelihood | false_positive_rate | false_negative_rate | true_positive_rate | true_negative_rate | positive_predictive_value | negative_predictive_value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 | 5.000000 |
| mean | 0.295261 | 0.704739 | 0.295273 | 0.704727 | 0.832707 | 0.716695 | 0.716723 | 0.716709 | 0.716723 | 0.881301 | 6.038613 | 0.321434 | 0.118699 | 0.283277 | 0.716723 | 0.881301 | 0.716695 | 0.881315 |
| std | 0.000146 | 0.000146 | 0.000161 | 0.000161 | 0.001417 | 0.002456 | 0.002485 | 0.002471 | 0.002485 | 0.000986 | 0.070457 | 0.003182 | 0.000986 | 0.002485 | 0.002485 | 0.000986 | 0.002456 | 0.001000 |
| min | 0.295080 | 0.704583 | 0.295080 | 0.704543 | 0.830316 | 0.712571 | 0.712571 | 0.712571 | 0.712571 | 0.879627 | 5.919679 | 0.318707 | 0.117938 | 0.281119 | 0.712571 | 0.879627 | 0.712571 | 0.879627 |
| 25% | 0.295176 | 0.704599 | 0.295176 | 0.704583 | 0.832565 | 0.716435 | 0.716435 | 0.716435 | 0.716435 | 0.881213 | 6.031237 | 0.319660 | 0.118187 | 0.281880 | 0.716435 | 0.881213 | 0.716435 | 0.881213 |
| 50% | 0.295232 | 0.704768 | 0.295232 | 0.704768 | 0.833343 | 0.717607 | 0.717607 | 0.717607 | 0.717607 | 0.881790 | 6.070604 | 0.320250 | 0.118210 | 0.282393 | 0.717607 | 0.881790 | 0.717607 | 0.881790 |
| 75% | 0.295401 | 0.704824 | 0.295417 | 0.704824 | 0.833455 | 0.718120 | 0.718120 | 0.718120 | 0.718120 | 0.881813 | 6.076135 | 0.321790 | 0.118787 | 0.283565 | 0.718120 | 0.881813 | 0.718120 | 0.881813 |
| max | 0.295417 | 0.704920 | 0.295457 | 0.704920 | 0.833858 | 0.718744 | 0.718881 | 0.718812 | 0.718881 | 0.882062 | 6.095409 | 0.326762 | 0.120373 | 0.287429 | 0.718881 | 0.882062 | 0.718744 | 0.882132 |
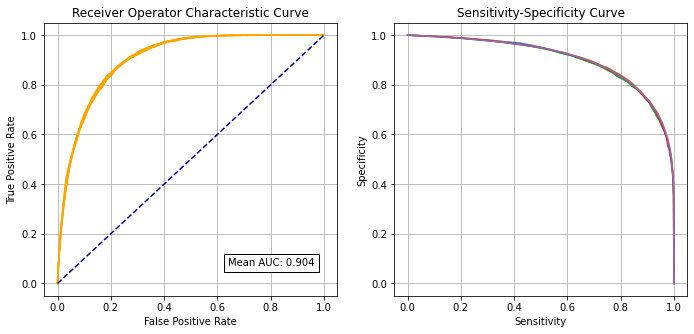
Receiver Operator Characteristic and Sensitivity-Specificity Curves#
Receiver Operator Characteristic Curve:
# Set up lists for results
k_fold_fpr = [] # false positive rate
k_fold_tpr = [] # true positive rate
k_fold_thresholds = [] # threshold applied
k_fold_auc = [] # area under curve
# Loop through k fold predictions and get ROC results
for i in range(5):
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(observed[i], predicted_proba[i])
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
k_fold_fpr.append(fpr)
k_fold_tpr.append(tpr)
k_fold_thresholds.append(thresholds)
k_fold_auc.append(roc_auc)
print (f'Run {i} AUC {roc_auc:0.4f}')
# Show mean area under curve
mean_auc = np.mean(k_fold_auc)
sd_auc = np.std(k_fold_auc)
print (f'\nMean AUC: {mean_auc:0.4f}')
print (f'SD AUC: {sd_auc:0.4f}')
Run 0 AUC 0.9035
Run 1 AUC 0.9056
Run 2 AUC 0.9014
Run 3 AUC 0.9036
Run 4 AUC 0.9045
Mean AUC: 0.9037
SD AUC: 0.0014
Sensitivity-specificity curve:
k_fold_sensitivity = []
k_fold_specificity = []
for i in range(5):
# Get classificiation probabilities for k-fold replicate
obs = observed[i]
proba = predicted_proba[i]
# Set up list for accuracy measures
sensitivity = []
specificity = []
# Loop through increments in probability of survival
thresholds = np.arange(0.0, 1.01, 0.01)
for cutoff in thresholds: # loop 0 --> 1 on steps of 0.1
# Get classificiation using cutoff
predicted_class = proba >= cutoff
predicted_class = predicted_class * 1.0
# Call accuracy measures function
accuracy = calculate_accuracy(obs, predicted_class)
# Add accuracy scores to lists
sensitivity.append(accuracy['sensitivity'])
specificity.append(accuracy['specificity'])
# Add replicate to lists
k_fold_sensitivity.append(sensitivity)
k_fold_specificity.append(specificity)
Combined plot:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
# Plot ROC
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
for i in range(5):
ax1.plot(k_fold_fpr[i], k_fold_tpr[i], color='orange')
ax1.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='darkblue', linestyle='--')
ax1.set_xlabel('False Positive Rate')
ax1.set_ylabel('True Positive Rate')
ax1.set_title('Receiver Operator Characteristic Curve')
text = f'Mean AUC: {mean_auc:.3f}'
ax1.text(0.64,0.07, text,
bbox=dict(facecolor='white', edgecolor='black'))
plt.grid(True)
# Plot sensitivity-specificity
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
for i in range(5):
ax2.plot(k_fold_sensitivity[i], k_fold_specificity[i])
ax2.set_xlabel('Sensitivity')
ax2.set_ylabel('Specificity')
ax2.set_title('Sensitivity-Specificity Curve')
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout(pad=2)
plt.savefig('./output/lr_single_fit_roc_sens_spec.jpg', dpi=300)
plt.show()
Identify cross-over of sensitivity and specificity#
sens = np.array(k_fold_sensitivity).mean(axis=0)
spec = np.array(k_fold_specificity).mean(axis=0)
df = pd.DataFrame()
df['sensitivity'] = sens
df['specificity'] = spec
df['spec greater sens'] = spec > sens
# find last index for senitivity being greater than specificity
mask = df['spec greater sens'] == False
last_id_sens_greater_spec = np.max(df[mask].index)
locs = [last_id_sens_greater_spec, last_id_sens_greater_spec + 1]
points = df.iloc[locs][['sensitivity', 'specificity']]
# Get intersetction with line of x=y
a1 = list(points.iloc[0].values)
a2 = list(points.iloc[1].values)
b1 = [0, 0]
b2 = [1, 1]
intersect = get_intersect(a1, a2, b1, b2)[0]
print(f'\nIntersect: {intersect:0.3f}')
Intersect: 0.820
Collate and save results#
hospital_results = []
kfold_result = []
threshold_results = []
observed_results = []
prob_results = []
predicted_results = []
for i in range(5):
hospital_results.extend(list(test_data[i]['StrokeTeam']))
kfold_result.extend(list(np.repeat(i, len(test_data[i]))))
threshold_results.extend(list(np.repeat(thresholds[i], len(test_data[i]))))
observed_results.extend(list(observed[i]))
prob_results.extend(list(predicted_proba[i]))
predicted_results.extend(list(predicted[i]))
single_model = pd.DataFrame()
single_model['hospital'] = hospital_results
single_model['observed'] = np.array(observed_results) * 1.0
single_model['prob'] = prob_results
single_model['predicted'] = predicted_results
single_model['k_fold'] = kfold_result
single_model['threshold'] = threshold_results
single_model['correct'] = single_model['observed'] == single_model['predicted']
# Save
filename = './predictions/single_fit_rf_k_fold.csv'
single_model.to_csv(filename, index=False)
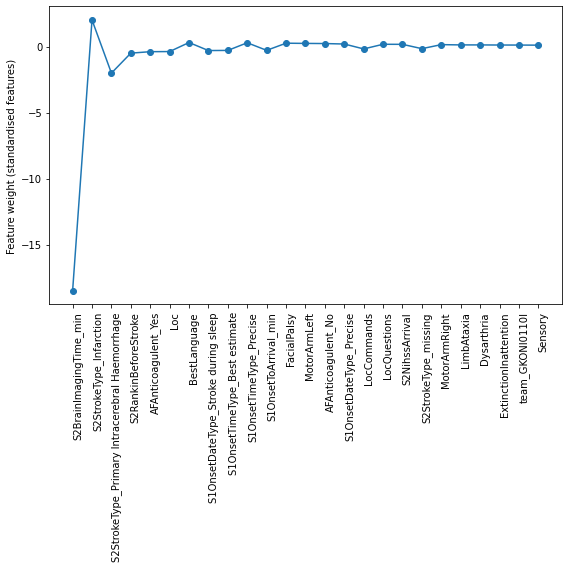
Feature Weights#
Get Logistic Regression weights (average across k-fold results). Sort by absolute value of weight.
features = X_test.columns.values
# Get average feature importance from k-fold
weights = np.array(feature_weights).mean(axis = 0)
weights = pd.DataFrame(data = weights, index=features)
weights.columns = ['weight']
weights['abs_weight'] = abs(weights['weight'])
# Sort by importance (weight)
weights.sort_values(by='abs_weight', ascending=False, inplace=True)
# Save
weights.to_csv('output/lr_single_fit_feature_weights.csv')
# Display top 25
weights.head(25)
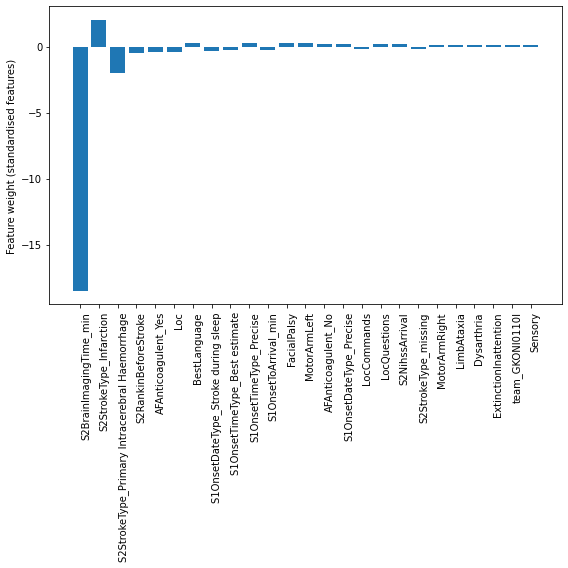
| weight | abs_weight | |
|---|---|---|
| S2BrainImagingTime_min | -18.492408 | 18.492408 |
| S2StrokeType_Infarction | 2.017887 | 2.017887 |
| S2StrokeType_Primary Intracerebral Haemorrhage | -2.009112 | 2.009112 |
| S2RankinBeforeStroke | -0.496542 | 0.496542 |
| AFAnticoagulent_Yes | -0.386646 | 0.386646 |
| Loc | -0.376646 | 0.376646 |
| BestLanguage | 0.307656 | 0.307656 |
| S1OnsetDateType_Stroke during sleep | -0.300494 | 0.300494 |
| S1OnsetTimeType_Best estimate | -0.289682 | 0.289682 |
| S1OnsetTimeType_Precise | 0.289682 | 0.289682 |
| S1OnsetToArrival_min | -0.284414 | 0.284414 |
| FacialPalsy | 0.256865 | 0.256865 |
| MotorArmLeft | 0.240609 | 0.240609 |
| AFAnticoagulent_No | 0.229443 | 0.229443 |
| S1OnsetDateType_Precise | 0.194409 | 0.194409 |
| LocCommands | -0.177114 | 0.177114 |
| LocQuestions | 0.174857 | 0.174857 |
| S2NihssArrival | 0.170151 | 0.170151 |
| S2StrokeType_missing | -0.157478 | 0.157478 |
| MotorArmRight | 0.147164 | 0.147164 |
| LimbAtaxia | 0.126763 | 0.126763 |
| Dysarthria | 0.125942 | 0.125942 |
| ExtinctionInattention | 0.117928 | 0.117928 |
| team_GKONI0110I | 0.115632 | 0.115632 |
| Sensory | 0.107787 | 0.107787 |
Line chart:
# Set up figure
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
# Get labels and values
labels = weights.index.values[0:25]
val = weights['weight'].values[0:25]
# Plot
ax.plot(val, marker='o')
ax.set_ylabel('Feature weight (standardised features)')
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(len(labels)))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
# Rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=90, ha="right",
rotation_mode="anchor")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('output/lr_single_fit_feature_weights_line.jpg', dpi=300)
plt.show()
Bar chart:
# Set up figure
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
# Get labels and values
labels = weights.index.values[0:25]
pos = np.arange(len(labels))
val = weights['weight'].values[0:25]
# Plot
ax.bar(pos, val)
ax.set_ylabel('Feature weight (standardised features)')
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(len(labels)))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
# Rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=90, ha="right",
rotation_mode="anchor")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('output/lr_single_fit_feature_weights_bar.jpg', dpi=300)
plt.show()
Learning cvurve#
Examine the relationship between training data size and accuracy.
# Set up list to collect results
results_training_size = []
results_accuracy = []
results_all_accuracy = []
# Get maximum training size (number of training records)
max_training_size = train_data[0].shape[0]
# Construct training sizes (values closer at lower end)
train_sizes = [50, 100, 250, 500, 1000, 2500]
for i in range (5000, max_training_size, 5000):
train_sizes.append(i)
# Loop through training sizes
for train_size in train_sizes:
# Record accuracy across k-fold replicates
replicate_accuracy = []
for replicate in range(5):
# Get training and test data (from first k-fold split)
train = train_data[0]
test = test_data[0]
# One hot encode hospitals
train_hosp = pd.get_dummies(train['StrokeTeam'], prefix = 'team')
train = pd.concat([train, train_hosp], axis=1)
train.drop('StrokeTeam', axis=1, inplace=True)
test_hosp = pd.get_dummies(test['StrokeTeam'], prefix = 'team')
test = pd.concat([test, test_hosp], axis=1)
test.drop('StrokeTeam', axis=1, inplace=True)
# Sample from training data
train = train.sample(n=train_size)
# Get X and y
X_train = train.drop('S2Thrombolysis', axis=1)
X_test = test.drop('S2Thrombolysis', axis=1)
y_train = train['S2Thrombolysis']
y_test = test['S2Thrombolysis']
# Standardise X data
X_train_std, X_test_std = standardise_data(X_train, X_test)
# Define and Fit model
model = LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs')
model.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
# Predict test set
y_pred_test = model.predict(X_test_std)
# Get accuracy and record results
accuracy = np.mean(y_pred_test == y_test)
replicate_accuracy.append(accuracy)
results_all_accuracy.append(accuracy)
# Store mean accuracy across the k-fold splits
results_accuracy.append(np.mean(replicate_accuracy))
results_training_size.append(train_size)
k_fold_accuracy = np.array(results_all_accuracy).reshape(len(train_sizes), 5)
Plot learning curve
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
for i in range(5):
ax1.plot(results_training_size, k_fold_accuracy[:, i])
ax1.set_xlabel('Training set size')
ax1.set_ylabel('Accuracy)')
# Focus on first 5000
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
for i in range(5):
ax2.plot(results_training_size, k_fold_accuracy[:, i])
ax2.set_xlabel('Training set size')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax2.set_xlim(0, 5000)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('./output/lr_single_learning_curve.jpg', dpi=300)
plt.show()
Calibration and assessment of accuracy when model has high confidence#
# Collate results in Dataframe
reliability_collated = pd.DataFrame()
# Loop through k fold predictions
for i in range(5):
# Get observed class and predicted probability
obs = observed[i]
prob = predicted_proba[i]
# Bin data with numpy digitize (this will assign a bin to each case)
step = 0.10
bins = np.arange(step, 1+step, step)
digitized = np.digitize(prob, bins)
# Put single fold data in DataFrame
reliability = pd.DataFrame()
reliability['bin'] = digitized
reliability['probability'] = prob
reliability['observed'] = obs
classification = 1 * (prob > 0.5 )
reliability['correct'] = obs == classification
reliability['count'] = 1
# Summarise data by bin in new dataframe
reliability_summary = pd.DataFrame()
# Add bins and k-fold to summary
reliability_summary['bin'] = bins
reliability_summary['k-fold'] = i
# Calculate mean of predicted probability of thrombolysis in each bin
reliability_summary['confidence'] = \
reliability.groupby('bin').mean()['probability']
# Calculate the proportion of patients who receive thrombolysis
reliability_summary['fraction_positive'] = \
reliability.groupby('bin').mean()['observed']
# Calculate proportion correct in each bin
reliability_summary['fraction_correct'] = \
reliability.groupby('bin').mean()['correct']
# Calculate fraction of results in each bin
reliability_summary['fraction_results'] = \
reliability.groupby('bin').sum()['count'] / reliability.shape[0]
# Add k-fold results to DatafRame collation
reliability_collated = reliability_collated.append(reliability_summary)
# Get mean results
reliability_summary = reliability_collated.groupby('bin').mean()
reliability_summary.drop('k-fold', axis=1, inplace=True)
reliability_summary
Plot results:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
# Plot predicted prob vs fraction psotive
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,1)
# Loop through k-fold reliability results
for i in range(5):
mask = reliability_collated['k-fold'] == i
k_fold_result = reliability_collated[mask]
x = k_fold_result['confidence']
y = k_fold_result['fraction_positive']
ax1.plot(x,y, color='orange')
# Add 1:1 line
ax1.plot([0,1],[0,1], color='k', linestyle ='--')
# Refine plot
ax1.set_xlabel('Model probability')
ax1.set_ylabel('Fraction positive')
ax1.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 1)
# Plot accuracy vs probability
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,2)
# Loop through k-fold reliability results
for i in range(5):
mask = reliability_collated['k-fold'] == i
k_fold_result = reliability_collated[mask]
x = k_fold_result['confidence']
y = k_fold_result['fraction_correct']
ax2.plot(x,y, color='orange')
# Refine plot
ax2.set_xlabel('Model probability')
ax2.set_ylabel('Fraction correct')
ax2.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax2.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax3 = ax2.twinx() # instantiate a second axes that shares the same x-axis
for i in range(5):
mask = reliability_collated['k-fold'] == i
k_fold_result = reliability_collated[mask]
x = k_fold_result['confidence']
y = k_fold_result['fraction_results']
ax3.plot(x,y, color='blue')
ax3.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax3.set_ylim(0, 0.5)
ax3.set_ylabel('Fraction of samples')
custom_lines = [Line2D([0], [0], color='orange', alpha=0.6, lw=2),
Line2D([0], [0], color='blue', alpha = 0.6,lw=2)]
plt.legend(custom_lines, ['Fraction correct', 'Fraction of samples'],
loc='upper center')
plt.tight_layout(pad=2)
plt.savefig('./output/lr_single_reliability.jpg', dpi=300)
plt.show()
Get accuracy of model when model is at least 80% confident
bins = [0.1, 0.2, 0.9, 1.0]
acc = reliability_summary.loc[bins].mean()['fraction_correct']
frac = reliability_summary.loc[bins].sum()['fraction_results']
print ('For samples with at least 80% confidence:')
print (f'Proportion of all samples: {frac:0.3f}')
print (f'Accuracy: {acc:0.3f}')
Observations#
Overall accuracy = 83.2% (89.6% for those 60% samples with at least 80% confidence of model)
Using nominal threshold (50% probability), specificity (88%) is greater than sensitivity (72%)
The model can achieve 82.0% sensitivity and specificity simultaneously
ROC AUC = 0.904
Only marginal improvements are made above a training set size of 20k
Key features predicting use of thrombolysis are:
Time from arrival to scan
Stroke type
Disability before stroke
Presence of AFAnticoagulent_Yes
Level of consciousness
The model shows good calibration of probability vs. fraction positive, without need of additional calibration